Likely there is a bug in your shader. GTK has very little effect on OpenGL code. It is hard to give you any clear suggestions until you share the full code that has the problem. You may also want to look for a library that can parse and render OBJ files for you.
Also, the Khronos Discourse may be a better place to post general OpenGL questions.
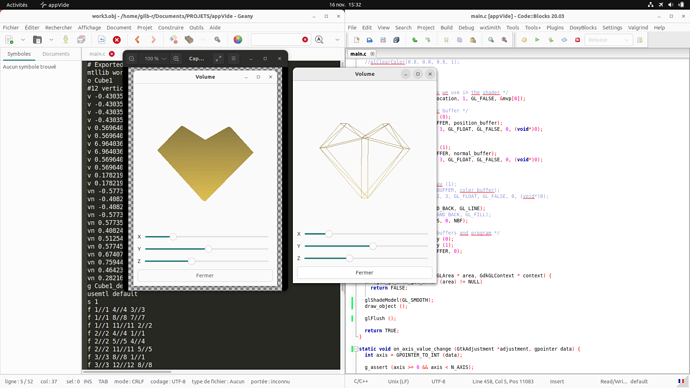
@jfrancis the shader I use is simply the one from GTK Demos GlArea example that is the basis of my code. But as it was only made for a triangle, it is maybe not well suited for a volume.
I already have my own code for parsing an OBJ as it is the main input of my application. Thank you for the link for Khronos Discourse, I will browse it to see if I can grab some answers there, maybe ask my question.
I assume you mean this one: glarea-gl.fs.glsl
That shader only does a color gradient based on screen position. To pass vertex colors you have to place those in a buffer somewhere, set vertex attributes to read them, then pass that to the output color in the shader. If none of this makes sense, I suggest reading an OpenGL tutorial like the ones here: https://learnopengl.com/
Yes, that’s this one. I tried to work with vertex colors, with the help of one of those tutorials you mentioned (Tutorial 4 : A Colored Cube) but I’m certainly missing something. I will try again ASAP as at first I didn’t add normals that I have now added. Thank you again for your help. It’s both my first GTK application and my first use of OpenGL, so I need to learn lots of things.
You only need normals if you are calculating shading and lighting, which will complicate your shader. For a simple flat shaded cube only the color is needed. Notice how the shaders in that example only pass the color through from the attribute.
I’m currently trying to understand how to use the same shaders as the Gears example, but it is quite a complex piece of code.
My unfolder project comes from an OpenJSCAD script that I wrote years ago. OpenJSCAD (now JSCAD, https://openjscad.xyz/ ) is a website that allows the user to write and execute javascript code that can create 3d/2d designs. It is handy to create parametric designs, like the GTK Demos Gears example could be. My long term goal is to port all my OpenJSCAD code to GTK, for sure it won’t be easy, but seeing this Gears example makes me think that it is not out of reach.
Well, I’m still trying to make it work. I found a shader (here : glsl - OpenGL shader to shade each face similar to MeshLab's visualizer - Stack Overflow) that would be enough for my needs, and tried to implement it, I think I correctly fill the arrays with the vertices positions, normals and colors, but the vertex shader needs separated matrix for projection, model and view, I tried to add them after the mvp matrix using the same logic as init_shaders () does for mvp, but when I use them into the shader I have nothing, so I think that my implementation is wrong.
I added the shaders code into strings because I didn’t manage to make “g_resources_lookup_data()” work. I’m using code::blocks as compiler with usual pkg-config for gtk4, I mean pkg-config --cflags gtk4for compiler options and pkg-config --libs gtk4 -lm -lepoxy for linker options.
Maybe is it possible to use mvp to extract model, view and projection matrices into the vertex shader ? or is it something that must be avoided ? Or is ot possible to change compute_mvp so that we also have those matrices ? I will try to ask for help on khronos forum as I understand that my question is out of the scope of GTK.
Here’s my code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gtk/gtk.h>
#include <epoxy/gl.h>static GtkWidget *gl_area = NULL;
enum {
X_AXIS,
Y_AXIS,
Z_AXIS,N_AXIS
};#define NBF 60
/* Rotation angles on each axis */
static float rotation_angles[N_AXIS] = { 0.0 };static void close_window (GtkWidget widget) {
/ Reset the state */
gl_area = NULL;rotation_angles[X_AXIS] = 0.0;
rotation_angles[Y_AXIS] = 0.0;
rotation_angles[Z_AXIS] = 0.0;
}/* Initialize the GL buffers */
static void init_buffers (GLuint *vao_out, GLuint *buffer_out, GLuint *normal_buffer_out, GLuint *color_buffer_out) {
GLuint vao, vertex_buffer, normal_buffer, color_buffer;// from simple polyhedron made with Wings 3d and saved to .obj file
GLfloat vertex_base = {
-0.43035963, -0.10000000, -0.56964037,
-0.43035963, -0.10000000, 0.43035963,
-0.43035963, 0.10000000, -0.56964037,
-0.43035963, 0.10000000, 0.43035963,
0.56964037, -0.10000000, 0.43035963,
0.56964037, 0.10000000, 0.43035963,
6.9640366e-2, -0.10000000, -0.56964037,
6.9640366e-2, 0.10000000, -0.56964037,
0.56964037, -0.10000000, -6.9640366e-2,
0.56964037, 0.10000000, -6.9640366e-2,
0.17821901, -0.10000000, -0.17821901,
0.17821901, 0.10000000, -0.17821901
};GLfloat normal_base = {
-0.57735027, -0.57735027, -0.57735027,
-0.40824829, -0.81649658, 0.40824829,
-0.40824829, 0.81649658, -0.40824829,
-0.57735027, 0.57735027, 0.57735027,
0.57735027, -0.57735027, 0.57735027,
0.40824829, 0.81649658, 0.40824829,
0.51254517, -0.53189952, -0.67407740,
0.57745853, 0.29963205, -0.75944867,
0.67407740, -0.53189952, -0.51254517,
0.75944867, 0.29963205, -0.57745853,
0.46423835, -0.75429803, -0.46423835,
0.28216632, 0.91693202, -0.28216632
};GLshort indices = {
1,4,3,
1,8,7,
1,11,2,
2,4,1,
2,5,4,
2,11,5,
3,8,1,
3,12,8,
4,5,6,
4,12,3,
5,10,6,
5,11,9,
6,12,4,
7,11,1,
8,11,7,
9,10,5,
10,11,12,
10,12,6,
11,10,9,
12,11,8
};GLfloat color_base = { // 1 color per face (hand created)
0.0, 0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 1.0,
0.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0, 0.0,
1.0, 0.0, 0.0,
1.0, 0.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 0.0,
1.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.5,
0.0, 0.0, 0.5,
0.0, 0.5, 0.0,
0.0, 0.5, 0.0,
0.0, 0.5, 0.5,
0.0, 0.5, 0.5,
0.0, 0.5, 1.0,
0.0, 0.5, 1.0,
};int nbV = NBF *3;
// POINTS
GLfloat vertex_data[nbV];// NORMALS
GLfloat normal_data[nbV];// COLORS
GLfloat color_data[nbV];// create arrays with unique values
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < NBF; i++) {
int o = (indices[i]-1) * 3;
for (int j =0; j < 3; j++) {
vertex_data[n] = vertex_base[o+j];
normal_data[n] = normal_base[o+j];
color_data [n] = color_base[o+j];
n++;
}
}// We only use one VAO, so we always keep it bound
glGenVertexArrays (1, &vao);
glBindVertexArray (vao);glEnableClientState (GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
// vertices
glGenBuffers (1, &vertex_buffer);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertex_buffer);
glBufferData (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof (vertex_data), vertex_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);// normals
glEnableClientState (GL_NORMAL_ARRAY);
glGenBuffers (1, &normal_buffer);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normal_buffer);
glBufferData (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof (normal_data), normal_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);// colors
glEnableClientState (GL_COLOR_ARRAY);
glGenBuffers (1, &color_buffer);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, color_buffer);
glBufferData (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof (color_data), color_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);if (vao_out != NULL)
*vao_out = vao;if (buffer_out != NULL)
*buffer_out = vertex_buffer;if (normal_buffer_out != NULL)
*normal_buffer_out = normal_buffer;if (color_buffer_out != NULL)
*color_buffer_out = color_buffer;
}/* Create and compile a shader */
static GLuint create_shader (int type, const char *src) {
GLuint shader;
int status;shader = glCreateShader (type);
glShaderSource (shader, 1, &src, NULL);
glCompileShader (shader);glGetShaderiv (shader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &status);
if (status == GL_FALSE) {
int log_len;
char *buffer;glGetShaderiv (shader, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &log_len); buffer = g_malloc (log_len + 1); glGetShaderInfoLog (shader, log_len, NULL, buffer); g_warning ("Compile failure in %s shader:\n%s", type == GL_VERTEX_SHADER ? "vertex" : "fragment", buffer); g_free (buffer); glDeleteShader (shader); return 0;}
return shader;
}/* Initialize the shaders and link them into a program */
static void init_shaders (GLuint *program_out, GLuint *mvp_out,
GLuint *m_out, GLuint *v_out, GLuint *p_out) {
GLuint vertex, fragment;
GLuint program = 0;
GLuint mvp = 0;
GLuint m = 0;
GLuint v = 0;
GLuint p = 0;
int status;// gl_Position = mvp * vec4(in_position, 1);
vertex = create_shader (GL_VERTEX_SHADER,
“#version 330 core\n
uniform mat4 mvp;
uniform mat4 projection_matrix;
uniform mat4 model_matrix;
uniform mat4 view_matrix;
layout(location=0) in vec3 in_position;
layout(location=1) in vec3 in_normal;
layout(location=2) in vec3 in_color;
out vec4 color;
void main(void){
gl_Position = projection_matrix * view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_position, 1);
vec3 normal_cameraspace = normalize(( view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_normal,0)).xyz);
vec3 cameraVector = normalize(vec3(0, 0, 0) - (view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_position, 1)).xyz);
float cosTheta = clamp( dot( normal_cameraspace, cameraVector ), 0,1 );
color = vec4(0.3 * in_color.rgb + cosTheta * in_color.rgb, 1.0);
}”);if (vertex == 0) {
*program_out = 0;
return;
}fragment = create_shader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER,
“#version 330 core\n
in vec4 color; out vec4 out_frag_color;
void main(void){ out_frag_color = vec4(1.0f, 0.85f, 0.35f, 1.0f);
}”);
if (fragment == 0) {
glDeleteShader (vertex);
*program_out = 0;
return;
}program = glCreateProgram ();
glAttachShader (program, vertex);
glAttachShader (program, fragment);glLinkProgram (program);
glGetProgramiv (program, GL_LINK_STATUS, &status);
if (status == GL_FALSE) {
int log_len;
char *buffer;glGetProgramiv (program, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &log_len); buffer = g_malloc (log_len + 1); glGetProgramInfoLog (program, log_len, NULL, buffer); g_warning ("Linking failure:\n%s", buffer); g_free (buffer); glDeleteProgram (program); program = 0; goto out;}
/* Get the location of the “mvp” uniform */
mvp = glGetUniformLocation (program, “mvp”);
m = glGetUniformLocation( program, “model” );
v = glGetUniformLocation( program, “view” );
p = glGetUniformLocation( program, “projection” );glDetachShader (program, vertex);
glDetachShader (program, fragment);out:
glDeleteShader (vertex);
glDeleteShader (fragment);if (program_out != NULL)
*program_out = program;if (m_out != NULL)
*m_out = m;if (v_out != NULL)
*v_out = v;if (p_out != NULL)
*p_out = p;
}static void compute_mvp (float *res, float phi, float theta, float psi) {
float x = phi * (G_PI / 180.f);
float y = theta * (G_PI / 180.f);
float z = psi * (G_PI / 180.f);
float c1 = cosf (x), s1 = sinf (x);
float c2 = cosf (y), s2 = sinf (y);
float c3 = cosf (z), s3 = sinf (z);
float c3c2 = c3 * c2;
float s3c1 = s3 * c1;
float c3s2s1 = c3 * s2 * s1;
float s3s1 = s3 * s1;
float c3s2c1 = c3 * s2 * c1;
float s3c2 = s3 * c2;
float c3c1 = c3 * c1;
float s3s2s1 = s3 * s2 * s1;
float c3s1 = c3 * s1;
float s3s2c1 = s3 * s2 * c1;
float c2s1 = c2 * s1;
float c2c1 = c2 * c1;/* initialize to the identity matrix */
res[0] = 1.f; res[4] = 0.f; res[8] = 0.f; res[12] = 0.f;
res[1] = 0.f; res[5] = 1.f; res[9] = 0.f; res[13] = 0.f;
res[2] = 0.f; res[6] = 0.f; res[10] = 1.f; res[14] = 0.f;
res[3] = 0.f; res[7] = 0.f; res[11] = 0.f; res[15] = 1.f;/* apply all three rotations using the three matrices:
*
- ⎡ c3 s3 0 ⎤ ⎡ c2 0 -s2 ⎤ ⎡ 1 0 0 ⎤
- ⎢ -s3 c3 0 ⎥ ⎢ 0 1 0 ⎥ ⎢ 0 c1 s1 ⎥
- ⎣ 0 0 1 ⎦ ⎣ s2 0 c2 ⎦ ⎣ 0 -s1 c1 ⎦
*/
res[0] = c3c2; res[4] = s3c1 + c3s2s1; res[8] = s3s1 - c3s2c1; res[12] = 0.f;
res[1] = -s3c2; res[5] = c3c1 - s3s2s1; res[9] = c3s1 + s3s2c1; res[13] = 0.f;
res[2] = s2; res[6] = -c2s1; res[10] = c2c1; res[14] = 0.f;
res[3] = 0.f; res[7] = 0.f; res[11] = 0.f; res[15] = 1.f;
}static GLuint position_buffer;
static GLuint normal_buffer;
static GLuint color_buffer;
static GLuint program;
static GLuint mvp_location;
static GLuint m_location;
static GLuint v_location;
static GLuint p_location;/* We need to set up our state when we realize the GtkGLArea widget */
static void realize (GtkWidget *widget) {
gtk_gl_area_make_current (GTK_GL_AREA (widget));if (gtk_gl_area_get_error (GTK_GL_AREA (widget)) != NULL)
return;//init_buffers (NULL, &position_buffer, &color_buffer);
init_buffers (NULL, &position_buffer, &normal_buffer, &color_buffer);
init_shaders (&program, &mvp_location, &m_location, &v_location, &p_location);
}/* We should tear down the state when unrealizing */
static void unrealize (GtkWidget *widget) {
gtk_gl_area_make_current (GTK_GL_AREA (widget));if (gtk_gl_area_get_error (GTK_GL_AREA (widget)) != NULL)
return;glDeleteBuffers (1, &position_buffer);
//glDeleteBuffers (1, &color_buffer);
glDeleteProgram (program);
}static void draw_object (void) {
float mvp[16];
float m[16];
float v[16];
float p[16];/* Compute the model view projection matrix using the
- rotation angles specified through the GtkRange widgets
*/
compute_mvp (mvp, rotation_angles[X_AXIS], rotation_angles[Y_AXIS], rotation_angles[Z_AXIS]);glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);/* Use our shaders */
glUseProgram (program);/* Update the “mvp” matrix we use in the shader */
glUniformMatrix4fv (mvp_location, 1, GL_FALSE, &mvp[0]);
glUniformMatrix4fv (m_location, 1, GL_FALSE, &m[0]);
glUniformMatrix4fv (v_location, 1, GL_FALSE, &v[0]);
glUniformMatrix4fv (p_location, 1, GL_FALSE, &p[0]);/* Use the vertices in our buffer /
glEnableVertexAttribArray (0);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, position_buffer);
glVertexAttribPointer (0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void)0);// normales
glEnableVertexAttribArray (1);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normal_buffer);
glVertexAttribPointer (1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0);// couleurs
glEnableVertexAttribArray (1);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, color_buffer);
glVertexAttribPointer (2, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0);glShadeModel(GL_FLAT);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glDepthMask(true);glDrawArrays (GL_TRIANGLES, 0, NBF);
/* We finished using the buffers and program */
glDisableVertexAttribArray (0);
glDisableVertexAttribArray (1);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
glUseProgram (0);
}static gboolean render (GtkGLArea * area, GdkGLContext * context) {
if (gtk_gl_area_get_error (area) != NULL)
return FALSE;draw_object ();
glFlush ();
return TRUE;
}static void on_axis_value_change (GtkAdjustment *adjustment, gpointer data) {
int axis = GPOINTER_TO_INT (data);g_assert (axis >= 0 && axis < N_AXIS);
/* Update the rotation angle */
rotation_angles[axis] = gtk_adjustment_get_value (adjustment);/* Update the contents of the GL drawing area */
gtk_widget_queue_draw (gl_area);
}static GtkWidget * create_axis_slider (int axis) {
GtkWidget *box, *label, *slider;
GtkAdjustment *adj;
const char *text;box = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_HORIZONTAL, 0);
switch (axis) {
case X_AXIS:
text = “X”;
break;case Y_AXIS: text = "Y"; break; case Z_AXIS: text = "Z"; break; default: g_assert_not_reached ();}
label = gtk_label_new (text);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), label);
gtk_widget_show (label);adj = gtk_adjustment_new (0.0, 0.0, 360.0, 1.0, 12.0, 0.0);
g_signal_connect (adj, “value-changed”,
G_CALLBACK (on_axis_value_change),
GINT_TO_POINTER (axis));
slider = gtk_scale_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_HORIZONTAL, adj);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), slider);
gtk_widget_set_hexpand (slider, TRUE);
gtk_widget_show (slider);gtk_widget_show (box);
return box;
}static void activate(GtkApplication *app, gpointer user_data)
{
GtkWidget *window, *box, *button, *controls;
int i;window = gtk_application_window_new(app);
gtk_window_set_default_size(GTK_WINDOW(window), 400, 600);
gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (window), “Volume”);
g_signal_connect (window, “destroy”, G_CALLBACK (close_window), NULL);box = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL, FALSE);
gtk_widget_set_margin_start (box, 12);
gtk_widget_set_margin_end (box, 12);
gtk_widget_set_margin_top (box, 12);
gtk_widget_set_margin_bottom (box, 12);
gtk_box_set_spacing (GTK_BOX (box), 6);
gtk_window_set_child (GTK_WINDOW (window), box);gl_area = gtk_gl_area_new ();
gtk_widget_set_hexpand (gl_area, TRUE);
gtk_widget_set_vexpand (gl_area, TRUE);
gtk_widget_set_size_request (gl_area, 100, 200);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), gl_area);// We need to initialize and free GL resources, so we use
// the realize and unrealize signals on the widget
//
g_signal_connect (gl_area, “realize”, G_CALLBACK (realize), NULL);
g_signal_connect (gl_area, “unrealize”, G_CALLBACK (unrealize), NULL);// The main “draw” call for GtkGLArea
g_signal_connect (gl_area, “render”, G_CALLBACK (render), NULL);controls = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL, FALSE);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), controls);
gtk_widget_set_hexpand (controls, TRUE);for (i = 0; i < N_AXIS; i++)
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (controls), create_axis_slider (i));button = gtk_button_new_with_label (“Fermer”);
gtk_widget_set_hexpand (button, TRUE);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), button);
g_signal_connect_swapped (button, “clicked”, G_CALLBACK (gtk_window_destroy), window);gtk_widget_show(window);
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
GtkApplication *app;
int res;app = gtk_application_new(NULL, G_APPLICATION_DEFAULT_FLAGS);
g_signal_connect(app, “activate”, G_CALLBACK(activate), NULL);
res = g_application_run(G_APPLICATION(app), argc, argv);
g_object_unref(app);return res;
}
Just a few random suggestions. Do not use glMatrixMode, that function does nothing in modern OpenGL using shaders.
The uniform names must match exactly what is in the shader. For example it should be p = glGetUniformLocation( program, "projection_matrix" );. Also your code is not setting these right, they are getting set to uninitialized variables. You should not try to write 3D shaders until you have a firm understanding of the linear algebra involved. Normally you would construct each of those matrices separately. One thing you can do in GTK code to make it easier is use the vector and matrix types from graphene.
OpenGL will report errors to tell you what is going on, but all errors are silently ignored by default. See this page for some more tips on how to debug OpenGL problems: LearnOpenGL - Debugging
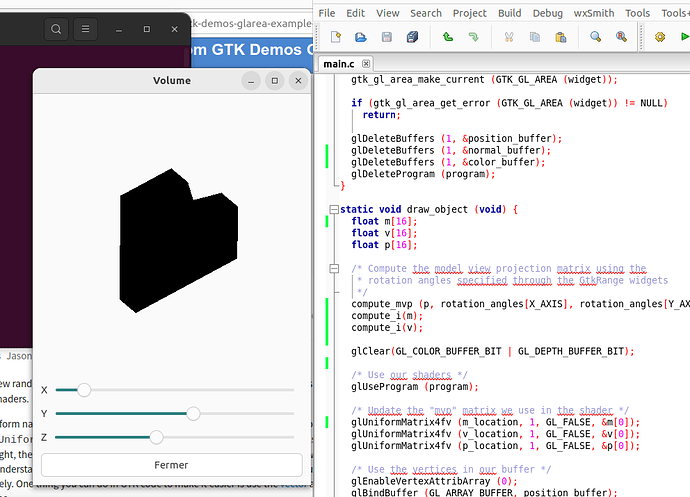
Thank you for your answers. I change the glGetUniformLocation () so they match the names used into the shader. It’s not a shader I’m writing, only a shader I found (link on previous post here) and what I’m doing is trying to implement it into my code. Now I remove the “mvp” uniform, setup “view_matrix” and “mode_matrix” uniforms as identity matrix, and setup “projection_matrix” just the same as “mvp” was (using compute_mvp () ). Now the model is rendered but all black. As I don’t see what I can add, I keep reading openGL tutorials and docs and dig the Khronos forums.
It was lacking color because of a typo that someone on StackExchange found.
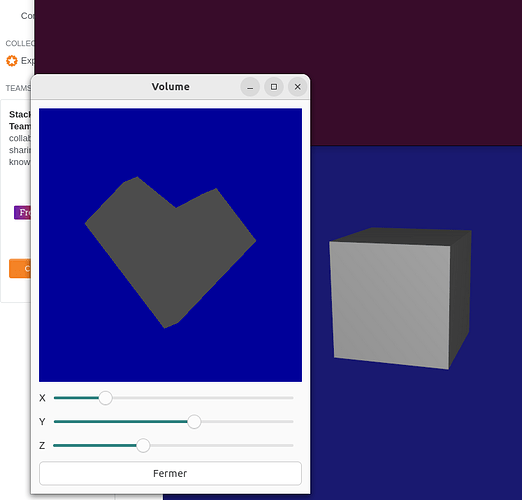
But the problem is not due to that. I’m using a model with all faces white (they appear gray) but the render is still with no shade. On the right of the capture is the way the shader make a white cube look.
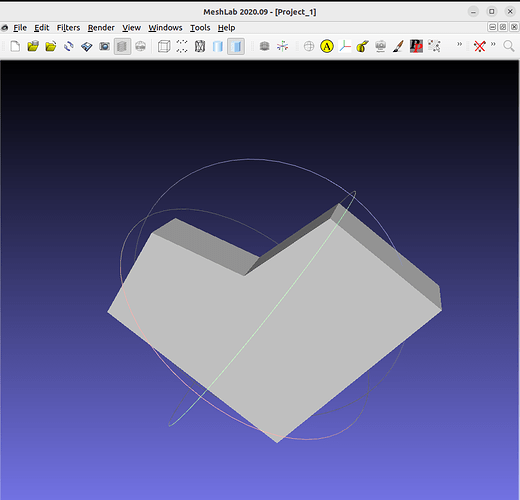
And here is how the model looks into MeshLab, thats’s what I’m trying to obtain.
When I was setting up GTK4, and discovered Graphene and Epoxy, I told myself that I need to use them on my projects, but I’m still looking for affordable examples to start from.
my code now
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gtk/gtk.h>
#include <epoxy/gl.h>
static GtkWidget *gl_area = NULL;
enum {
X_AXIS,
Y_AXIS,
Z_AXIS,
N_AXIS
};
#define NBF 60
/* Rotation angles on each axis */
static float rotation_angles[N_AXIS] = { 0.0 };
static void close_window (GtkWidget *widget) {
/* Reset the state */
gl_area = NULL;
rotation_angles[X_AXIS] = 0.0;
rotation_angles[Y_AXIS] = 0.0;
rotation_angles[Z_AXIS] = 0.0;
}
/* Initialize the GL buffers */
static void init_buffers (GLuint *vao_out, GLuint *buffer_out, GLuint *normal_buffer_out, GLuint *color_buffer_out) {
GLuint vao, vertex_buffer, normal_buffer, color_buffer;
// from simple polyhedron made with Wings 3d and saved to .obj file
GLfloat vertex_base[] = {
-0.43035963, -0.10000000, -0.56964037,
-0.43035963, -0.10000000, 0.43035963,
-0.43035963, 0.10000000, -0.56964037,
-0.43035963, 0.10000000, 0.43035963,
0.56964037, -0.10000000, 0.43035963,
0.56964037, 0.10000000, 0.43035963,
6.9640366e-2, -0.10000000, -0.56964037,
6.9640366e-2, 0.10000000, -0.56964037,
0.56964037, -0.10000000, -6.9640366e-2,
0.56964037, 0.10000000, -6.9640366e-2,
0.17821901, -0.10000000, -0.17821901,
0.17821901, 0.10000000, -0.17821901
};
GLfloat normal_base[] = {
-0.57735027, -0.57735027, -0.57735027,
-0.40824829, -0.81649658, 0.40824829,
-0.40824829, 0.81649658, -0.40824829,
-0.57735027, 0.57735027, 0.57735027,
0.57735027, -0.57735027, 0.57735027,
0.40824829, 0.81649658, 0.40824829,
0.51254517, -0.53189952, -0.67407740,
0.57745853, 0.29963205, -0.75944867,
0.67407740, -0.53189952, -0.51254517,
0.75944867, 0.29963205, -0.57745853,
0.46423835, -0.75429803, -0.46423835,
0.28216632, 0.91693202, -0.28216632
};
GLshort indices[] = {
1,4,3,
1,8,7,
1,11,2,
2,4,1,
2,5,4,
2,11,5,
3,8,1,
3,12,8,
4,5,6,
4,12,3,
5,10,6,
5,11,9,
6,12,4,
7,11,1,
8,11,7,
9,10,5,
10,11,12,
10,12,6,
11,10,9,
12,11,8
};
GLfloat color_base[] = { // 1 color per face (all white)
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0
};
/*GLfloat color_base[] = { // 1 color per face (hand created)
0.0, 0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 1.0,
0.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0, 0.0,
1.0, 0.0, 0.0,
1.0, 0.0, 1.0,
1.0, 0.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 0.0,
1.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.5,
0.0, 0.0, 0.5,
0.0, 0.5, 0.0,
0.0, 0.5, 0.0,
0.0, 0.5, 0.5,
0.0, 0.5, 0.5,
0.0, 0.5, 1.0,
0.0, 0.5, 1.0,
};*/
int nbV = NBF *3;
// POINTS
GLfloat vertex_data[nbV];
// NORMALS
GLfloat normal_data[nbV];
// COLORS
GLfloat color_data[nbV];
// create arrays with unique values
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < NBF; i++) {
int o = (indices[i]-1) * 3;
for (int j =0; j < 3; j++) {
vertex_data[n] = vertex_base[o+j];
normal_data[n] = normal_base[o+j];
color_data[n] = color_base[o+j];
n++;
}
}
// We only use one VAO, so we always keep it bound
glGenVertexArrays (1, &vao);
glBindVertexArray (vao);
glEnableClientState (GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
// vertices
glGenBuffers (1, &vertex_buffer);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertex_buffer);
glBufferData (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof (vertex_data), vertex_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// normals
glEnableClientState (GL_NORMAL_ARRAY);
glGenBuffers (1, &normal_buffer);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normal_buffer);
glBufferData (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof (normal_data), normal_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// colors
glEnableClientState (GL_COLOR_ARRAY);
glGenBuffers (1, &color_buffer);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, color_buffer);
glBufferData (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof (color_data), color_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
if (vao_out != NULL)
*vao_out = vao;
if (buffer_out != NULL)
*buffer_out = vertex_buffer;
if (normal_buffer_out != NULL)
*normal_buffer_out = normal_buffer;
if (color_buffer_out != NULL)
*color_buffer_out = color_buffer;
}
/* Create and compile a shader */
static GLuint create_shader (int type, const char *src) {
GLuint shader;
int status;
shader = glCreateShader (type);
glShaderSource (shader, 1, &src, NULL);
glCompileShader (shader);
glGetShaderiv (shader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &status);
if (status == GL_FALSE) {
int log_len;
char *buffer;
glGetShaderiv (shader, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &log_len);
buffer = g_malloc (log_len + 1);
glGetShaderInfoLog (shader, log_len, NULL, buffer);
g_warning ("Compile failure in %s shader:\n%s",
type == GL_VERTEX_SHADER ? "vertex" : "fragment",
buffer);
g_free (buffer);
glDeleteShader (shader);
return 0;
}
return shader;
}
/* Initialize the shaders and link them into a program */
static void init_shaders (GLuint *program_out, GLuint *m_out, GLuint *v_out, GLuint *p_out) {
GLuint vertex, fragment;
GLuint program = 0;
GLuint m = 0;
GLuint v = 0;
GLuint p = 0;
int status;
/*
//gl_Position = projection_matrix * view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_position, 1);\
//vec3 normal_cameraspace = normalize(( view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_normal,0)).xyz);\
//vec3 cameraVector = normalize(vec3(0, 0, 0) - (view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_position, 1)).xyz);\
//float cosTheta = clamp( dot( normal_cameraspace, cameraVector ), 0, 1 );\
//color = vec4(0.3 * in_color.rgb + cosTheta * in_color.rgb, 1);\
*/
vertex = create_shader (GL_VERTEX_SHADER,
"#version 330 core\n\
uniform mat4 projection_matrix;\
uniform mat4 model_matrix;\
uniform mat4 view_matrix;\
layout(location=0) in vec3 in_position;\
layout(location=1) in vec3 in_normal;\
layout(location=2) in vec3 in_color;\
out vec4 color;\
void main(void){\
gl_Position = projection_matrix * view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_position, 1);\
vec3 normal_cameraspace = normalize(( view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_normal,0)).xyz);\
vec3 cameraVector = normalize(vec3(0, 0, 0) - (view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(in_position, 1)).xyz);\
float cosTheta = clamp( dot( normal_cameraspace, cameraVector ), 0, 1 );\
color = vec4(0.3 * in_color.rgb + cosTheta * in_color.rgb, 1);\
}");
if (vertex == 0) {
*program_out = 0;
return;
}
fragment = create_shader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER,
"#version 330 core\n\
in vec4 color; out vec4 out_frag_color;\
void main(void){ out_frag_color = color;\
}");
if (fragment == 0) {
glDeleteShader (vertex);
*program_out = 0;
return;
}
program = glCreateProgram ();
glAttachShader (program, vertex);
glAttachShader (program, fragment);
glLinkProgram (program);
glGetProgramiv (program, GL_LINK_STATUS, &status);
if (status == GL_FALSE) {
int log_len;
char *buffer;
glGetProgramiv (program, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &log_len);
buffer = g_malloc (log_len + 1);
glGetProgramInfoLog (program, log_len, NULL, buffer);
g_warning ("Linking failure:\n%s", buffer);
g_free (buffer);
glDeleteProgram (program);
program = 0;
goto out;
}
/* Get the location of the "mvp" uniform */
m = glGetUniformLocation( program, "model_matrix" );
v = glGetUniformLocation( program, "view_matrix" );
p = glGetUniformLocation( program, "projection_matrix" );
glDetachShader (program, vertex);
glDetachShader (program, fragment);
out:
glDeleteShader (vertex);
glDeleteShader (fragment);
if (program_out != NULL)
*program_out = program;
if (m_out != NULL)
*m_out = m;
if (v_out != NULL)
*v_out = v;
if (p_out != NULL)
*p_out = p;
}
static void compute_i (float *res) {
/* initialize to the identity matrix */
res[0] = 1.f; res[4] = 0.f; res[8] = 0.f; res[12] = 0.f;
res[1] = 0.f; res[5] = 1.f; res[9] = 0.f; res[13] = 0.f;
res[2] = 0.f; res[6] = 0.f; res[10] = 1.f; res[14] = 0.f;
res[3] = 0.f; res[7] = 0.f; res[11] = 0.f; res[15] = 1.f;
}
static void compute_mvp (float *res, float phi, float theta, float psi) {
float x = phi * (G_PI / 180.f);
float y = theta * (G_PI / 180.f);
float z = psi * (G_PI / 180.f);
float c1 = cosf (x), s1 = sinf (x);
float c2 = cosf (y), s2 = sinf (y);
float c3 = cosf (z), s3 = sinf (z);
float c3c2 = c3 * c2;
float s3c1 = s3 * c1;
float c3s2s1 = c3 * s2 * s1;
float s3s1 = s3 * s1;
float c3s2c1 = c3 * s2 * c1;
float s3c2 = s3 * c2;
float c3c1 = c3 * c1;
float s3s2s1 = s3 * s2 * s1;
float c3s1 = c3 * s1;
float s3s2c1 = s3 * s2 * c1;
float c2s1 = c2 * s1;
float c2c1 = c2 * c1;
compute_i(res);
/* apply all three rotations using the three matrices:
*
* ⎡ c3 s3 0 ⎤ ⎡ c2 0 -s2 ⎤ ⎡ 1 0 0 ⎤
* ⎢ -s3 c3 0 ⎥ ⎢ 0 1 0 ⎥ ⎢ 0 c1 s1 ⎥
* ⎣ 0 0 1 ⎦ ⎣ s2 0 c2 ⎦ ⎣ 0 -s1 c1 ⎦
*/
res[0] = c3c2; res[4] = s3c1 + c3s2s1; res[8] = s3s1 - c3s2c1; res[12] = 0.f;
res[1] = -s3c2; res[5] = c3c1 - s3s2s1; res[9] = c3s1 + s3s2c1; res[13] = 0.f;
res[2] = s2; res[6] = -c2s1; res[10] = c2c1; res[14] = 0.f;
res[3] = 0.f; res[7] = 0.f; res[11] = 0.f; res[15] = 1.f;
}
static GLuint position_buffer;
static GLuint normal_buffer;
static GLuint color_buffer;
static GLuint program;
static GLuint m_location;
static GLuint v_location;
static GLuint p_location;
/* We need to set up our state when we realize the GtkGLArea widget */
static void realize (GtkWidget *widget) {
gtk_gl_area_make_current (GTK_GL_AREA (widget));
if (gtk_gl_area_get_error (GTK_GL_AREA (widget)) != NULL)
return;
init_buffers (NULL, &position_buffer, &normal_buffer, &color_buffer);
init_shaders (&program, &m_location, &v_location, &p_location);
}
/* We should tear down the state when unrealizing */
static void unrealize (GtkWidget *widget) {
gtk_gl_area_make_current (GTK_GL_AREA (widget));
if (gtk_gl_area_get_error (GTK_GL_AREA (widget)) != NULL)
return;
glDeleteBuffers (1, &position_buffer);
glDeleteBuffers (1, &normal_buffer);
glDeleteBuffers (1, &color_buffer);
glDeleteProgram (program);
}
static void draw_object (void) {
float m[16];
float v[16];
float p[16];
/* Compute the model view projection matrix using the
* rotation angles specified through the GtkRange widgets
*/
compute_mvp (p, rotation_angles[X_AXIS], rotation_angles[Y_AXIS], rotation_angles[Z_AXIS]);
compute_i(m);
compute_i(v);
glClearColor(0, 0, 0.6, 1);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
/* Use our shaders */
glUseProgram (program);
/* Update the "mvp" matrix we use in the shader */
glUniformMatrix4fv (m_location, 1, GL_FALSE, &m[0]);
glUniformMatrix4fv (v_location, 1, GL_FALSE, &v[0]);
glUniformMatrix4fv (p_location, 1, GL_FALSE, &p[0]);
/* Use the vertices in our buffer */
glEnableVertexAttribArray (0);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, position_buffer);
glVertexAttribPointer (0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0);
// normales
glEnableVertexAttribArray (1);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normal_buffer);
glVertexAttribPointer (1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0);
// couleurs
glEnableVertexAttribArray (2);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, color_buffer);
glVertexAttribPointer (2, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glRenderMode(GL_RENDER);
glDrawArrays (GL_TRIANGLES, 0, NBF);
/* We finished using the buffers and program */
glDisableVertexAttribArray (0);
glDisableVertexAttribArray (1);
glDisableVertexAttribArray (2);
glBindBuffer (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
glUseProgram (0);
}
static gboolean render (GtkGLArea * area, GdkGLContext * context) {
if (gtk_gl_area_get_error (area) != NULL)
return FALSE;
draw_object ();
glFlush ();
return TRUE;
}
static void on_axis_value_change (GtkAdjustment *adjustment, gpointer data) {
int axis = GPOINTER_TO_INT (data);
g_assert (axis >= 0 && axis < N_AXIS);
/* Update the rotation angle */
rotation_angles[axis] = gtk_adjustment_get_value (adjustment);
/* Update the contents of the GL drawing area */
gtk_widget_queue_draw (gl_area);
}
static GtkWidget * create_axis_slider (int axis) {
GtkWidget *box, *label, *slider;
GtkAdjustment *adj;
const char *text;
box = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_HORIZONTAL, 0);
switch (axis) {
case X_AXIS:
text = "X";
break;
case Y_AXIS:
text = "Y";
break;
case Z_AXIS:
text = "Z";
break;
default:
g_assert_not_reached ();
}
label = gtk_label_new (text);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), label);
gtk_widget_show (label);
adj = gtk_adjustment_new (0.0, 0.0, 360.0, 1.0, 12.0, 0.0);
g_signal_connect (adj, "value-changed",
G_CALLBACK (on_axis_value_change),
GINT_TO_POINTER (axis));
slider = gtk_scale_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_HORIZONTAL, adj);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), slider);
gtk_widget_set_hexpand (slider, TRUE);
gtk_widget_show (slider);
gtk_widget_show (box);
return box;
}
static void activate(GtkApplication *app, gpointer user_data)
{
GtkWidget *window, *box, *button, *controls;
int i;
window = gtk_application_window_new(app);
gtk_window_set_default_size(GTK_WINDOW(window), 400, 600);
gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (window), "Volume");
g_signal_connect (window, "destroy", G_CALLBACK (close_window), NULL);
box = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL, FALSE);
gtk_widget_set_margin_start (box, 12);
gtk_widget_set_margin_end (box, 12);
gtk_widget_set_margin_top (box, 12);
gtk_widget_set_margin_bottom (box, 12);
gtk_box_set_spacing (GTK_BOX (box), 6);
gtk_window_set_child (GTK_WINDOW (window), box);
gl_area = gtk_gl_area_new ();
gtk_widget_set_hexpand (gl_area, TRUE);
gtk_widget_set_vexpand (gl_area, TRUE);
gtk_widget_set_size_request (gl_area, 100, 200);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), gl_area);
// We need to initialize and free GL resources, so we use
// the realize and unrealize signals on the widget
//
g_signal_connect (gl_area, "realize", G_CALLBACK (realize), NULL);
g_signal_connect (gl_area, "unrealize", G_CALLBACK (unrealize), NULL);
// The main "draw" call for GtkGLArea
g_signal_connect (gl_area, "render", G_CALLBACK (render), NULL);
controls = gtk_box_new (GTK_ORIENTATION_VERTICAL, FALSE);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), controls);
gtk_widget_set_hexpand (controls, TRUE);
for (i = 0; i < N_AXIS; i++)
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (controls), create_axis_slider (i));
button = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Fermer");
gtk_widget_set_hexpand (button, TRUE);
gtk_box_append (GTK_BOX (box), button);
g_signal_connect_swapped (button, "clicked", G_CALLBACK (gtk_window_destroy), window);
gtk_widget_show(window);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
GtkApplication *app;
int res;
app = gtk_application_new(NULL, G_APPLICATION_DEFAULT_FLAGS);
g_signal_connect(app, "activate", G_CALLBACK(activate), NULL);
res = g_application_run(G_APPLICATION(app), argc, argv);
g_object_unref(app);
return res;
}
Examples can only show you so much. You would need to have an understanding of the math and terminology involved and then you can use any linear algebra package. Do not try to pull things from random tutorials, start from the first tutorials and work your way up slowly.
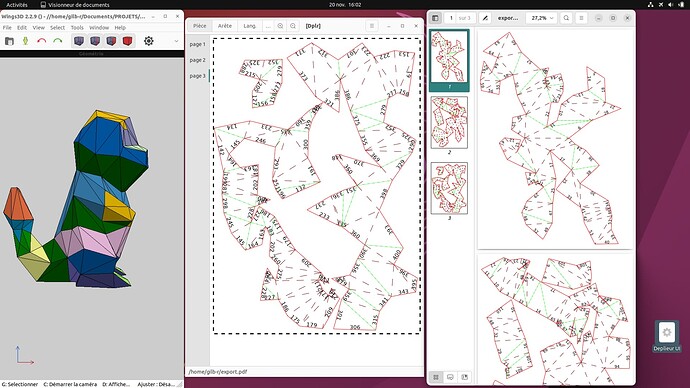
I’m not trying to do anything complex, here’s what I want to obtain
On the left is what I want to do with the glArea, display a model with faces colored to reflect the faces edition done with my application (in the middle) that allows to unfold the model into pieces (each piece with its own color. (on the right is the pdf output that the application does and is the purpose of the app).
This topic was automatically closed 30 days after the last reply. New replies are no longer allowed.